CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
DA8326855
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
Benzenepropanamine, N-methyl-gamma-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-, (+-)-
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
54910-89-3
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199801
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
9
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C17-H18-F3-N-O
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
309.36
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
60 mg/kg/21W-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Nutritional and Gross Metabolic - other changes
-
REFERENCE :
-
AJPSAO American Journal of Psychiatry. (American Psychiatric Assoc., Circulation Dept., 1400 K St., NW, Washington, DC 20005) V.78- 1921- Volume(issue)/page/year: 153,134,1996
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
72 mg/kg/26W-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - somnolence (general depressed activity)
-
REFERENCE :
-
JCPYDR Journal of Clinical Pyschopharmacology. (Williams & Wilkins Co., 428 E. Preston St., Baltimore, MD 21202) V.1- 1981- Volume(issue)/page/year: 10,343,1990
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
16800 ug/kg/6W-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - muscle weakness Behavioral - antipsychotic Nutritional and Gross Metabolic - other changes
-
REFERENCE :
-
AIMDAP Archives of Internal Medicine. (AMA, 535 N. Dearborn St., Chicago, IL 60610) V.1- 1908- Volume(issue)/page/year: 156,681,1996
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2 mg/kg/5D-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - somnolence (general depressed activity) Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - dyspnea Nutritional and Gross Metabolic - other changes
-
REFERENCE :
-
AIMDAP Archives of Internal Medicine. (AMA, 535 N. Dearborn St., Chicago, IL 60610) V.1- 1908- Volume(issue)/page/year: 156,681,1996
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
825 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
DRFUD4 Drugs of the Future. (J.R. Prous, S.A., Apartado de Correos 540, 08080 Barcelona, Spain) V.1- 1975/76- Volume(issue)/page/year: 15,1178,1990
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
121 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
DRFUD4 Drugs of the Future. (J.R. Prous, S.A., Apartado de Correos 540, 08080 Barcelona, Spain) V.1- 1975/76- Volume(issue)/page/year: 15,1178,1990
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
464 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
DRFUD4 Drugs of the Future. (J.R. Prous, S.A., Apartado de Correos 540, 08080 Barcelona, Spain) V.1- 1975/76- Volume(issue)/page/year: 15,1178,1990
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
87500 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
DRFUD4 Drugs of the Future. (J.R. Prous, S.A., Apartado de Correos 540, 08080 Barcelona, Spain) V.1- 1975/76- Volume(issue)/page/year: 15,1178,1990 ** REPRODUCTIVE DATA **
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
DOSE :
-
80 mg/kg
-
SEX/DURATION :
-
female 13-20 day(s) after conception
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Reproductive - Effects on Newborn - biochemical and metabolic
-
REFERENCE :
-
JPETAB Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. (Williams & Wilkins Co., 428 E. Preston St., Baltimore, MD 21202) V.1- 1909/10- Volume(issue)/page/year: 280,138,1997
|
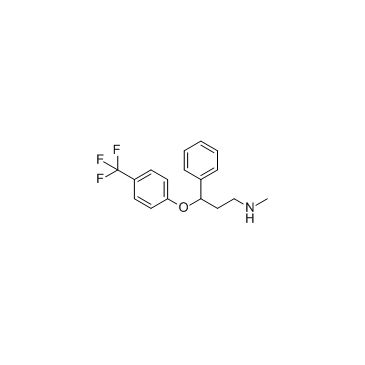
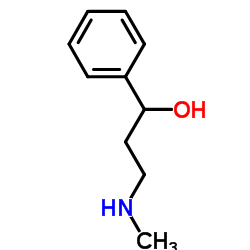 CAS#:42142-52-9
CAS#:42142-52-9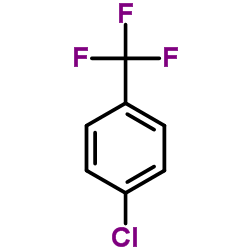 CAS#:98-56-6
CAS#:98-56-6![Ethyl N-methyl-N-[3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]carbamate Structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/159/204704-95-0.png) CAS#:204704-95-0
CAS#:204704-95-0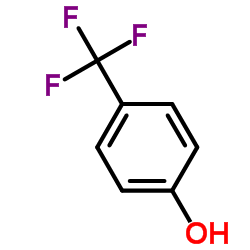 CAS#:402-45-9
CAS#:402-45-9![methyl-[3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]cyanamide Structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/003/57226-06-9.png) CAS#:57226-06-9
CAS#:57226-06-9 CAS#:936-59-4
CAS#:936-59-4 CAS#:56296-78-7
CAS#:56296-78-7 CAS#:18776-12-0
CAS#:18776-12-0 CAS#:62872-58-6
CAS#:62872-58-6 CAS#:114247-09-5
CAS#:114247-09-5