LOXITANE C
Modify Date: 2024-01-16 18:04:37
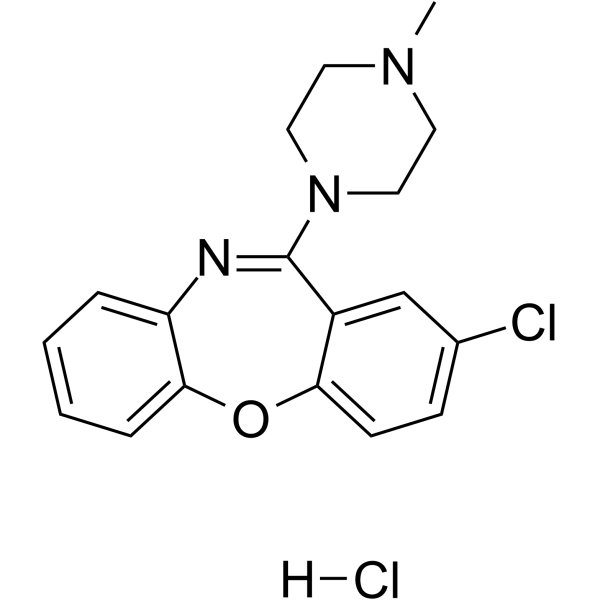
LOXITANE C structure
|
Common Name | LOXITANE C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54810-23-0 | Molecular Weight | 364.269 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 458.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H19Cl2N3O | Melting Point | 109-110ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 231.1ºC | |
Use of LOXITANE CLoxapine hydrochloride is an orally active dopamine inhibitor, 5-HT receptor antagonist and also a dibenzoxazepine anti-psychotic agent[1][4]. |
| Name | 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Loxapine hydrochloride is an orally active dopamine inhibitor, 5-HT receptor antagonist and also a dibenzoxazepine anti-psychotic agent[1][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
human 5-HT2 Human D4 Receptor Human D1 Receptor Human D2 Receptor |
| In Vitro | In the presence of Loxapine, [3H]ketanserin binds to 5-HT2 receptor in Frontal cortex of brain in human and bovine with Ki value of 6.2 nM and 6.6 nM, respectively. Loxapine has the rank order of potency for the various receptors appears to be as follows: 5-HT2≥D4>>>D1>D2 in comparing competition experiments involving the human membranes[1]. Loxapine (0-20 μM, 24 h or 72 h) reduces IL-1β secretion by LPS-activated mixed glia cultures, reduces IL-2 secretion in mixed glia cultures, and decreases IL-1β and IL-2 secretion in LPS-induced microglia cultures[2]. |
| In Vivo | Loxapine (5 mg/kg; i.p.; daily for 4 or 10 weeks) decreases serotonin (S2) but does not elevate dopamine (D2) receptor numbers in the rat brain[3]. Animal Model: Adult male Wistar rats (150-175 g)[3] Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection, daily for 4 or 10 weeks Result: Induced a very significant reduction (more than 50%) of serotonin (S2) receptor density after 4 weeks or 10 weeks of daily injection, but did not produce any significant increase in dopamine receptor density. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 458.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 109-110ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H19Cl2N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 364.269 |
| Flash Point | 231.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 363.090515 |
| PSA | 28.07000 |
| LogP | 3.88480 |
| 2-Chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine Monohydrochloride |
| Desconex (TN) |
| Dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine, 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| LOXITANE C |
| 2-Chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Dibenz(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine,2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-,monohydrochloride |
| Loxapine hydrochloride |
| Loxapine monohydrochloride |
| 2-Chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenz(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine monohydrochloride |
| Loxapine HCl |