osalmid

osalmid structure
|
Common Name | osalmid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 526-18-1 | Molecular Weight | 229.231 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 350.8±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11NO3 | Melting Point | 179ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 165.9±23.7 °C | |
Use of osalmidOsalmid is a ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2) targeting compound; suppresses ribonucleotide reductase activity with an IC50 of 8.23 μM. |
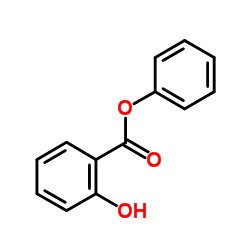
| Name | 2-Hydroxy-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-benzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Osalmid is a ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2) targeting compound; suppresses ribonucleotide reductase activity with an IC50 of 8.23 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 8.23 μM (ribonucleotide reductase)[1] |
| In Vitro | Osalmid is identified as a potential ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2) compound. Osalmid is 10-fold more active in inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity than hydroxyurea, and significantly inhibits HBV DNA and cccDNA synthesis in HepG2.2.15 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. After treatment for 8 days with Osalmid, the EC50 for HBV DNA inhibition are 11.1 μM for culture supernatant and 16.5 μM for cells. Osalmid suppresses RR activity in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 8.23 μM. Osalmid is shown to possess potent activity against a 3TC-resistant HBV strain, suggesting utility in treating drug-resistant HBV infections[1]. |
| In Vivo | Osalmid reduces RR activity and HBV replication in HBV-transgenic mice and shows a synergistic efficacy with 3TC without significant toxicity. Oral dosing of osalmid at 400 mg/kg/d results in a time-dependent inhibition of HBV DNA replication. After treatment for 4 weeks, osalmid suppresses HBV DNA replication by about 40-45% as compared to the control in mouse sera and liver tissues[1]. |
| Cell Assay | HepG2.2.15 cells are cultured in the presence of 200 μg/mL G418. Cell viability is determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 in 96-well plates treated with Osalmid for designated times. For long term assays, the culture supernatants are replaced with fresh media containing Osalmid every two days. The control wells contained equivalent amounts of DMSO. The CC50 is calculated as the concentration of a compound that reduced the cell viability to 50% compared to the control[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: The HBV-transgenic mouse lineage is initially produced on a BALB/c background. Osalmid or 3TC is suspended in 0.05% CMC-Na and administered once a day by gavage at 400 and 100 mg/kg, respectively, for 28 days. For the combination group, mice are intragastrically administered with a mixture of osalmid and 3TC. 0.05% CMC-Na solution is used as control. The mouse sera are collected and assayed for HBV DNA levels and AST/ALT activity. Mice are then sacrificed after the 28-day drug treatment and the livers are excised for analysis[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 350.8±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 179ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 229.231 |
| Flash Point | 165.9±23.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 229.073898 |
| PSA | 69.56000 |
| LogP | 2.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.711 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~48% 
osalmid CAS#:526-18-1 |
| Literature: Kumar, Anil; Narasimhan, Balasubramanian; Kumar, Devinder Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2007 , vol. 15, # 12 p. 4113 - 4124 |
|
~% 
osalmid CAS#:526-18-1 |
| Literature: Fargher; Galloway; Probert J.Textile Inst., 1930 , vol. 21, p. 245T,255T |
|
~% 
osalmid CAS#:526-18-1 |
| Literature: Weizmann; Bergmann; Sulzbacher Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1948 , vol. 13, p. 796,799 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
| MFCD00020026 |
| bilene |
| osalmid |
| bilocol |
| 2-Hydroxy-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzamide |
| Qsalmid |
| auxobil |
| EINECS 208-385-9 |
| LOIRD |
| 2-Hydroxy-N-(4-Hydroxy Phenyl)Benzamide |
| driol |
| phps |
| l1718 |
| Benzamide, 2-hydroxy-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- |
| 4'-HYDROXYSALICYLANILIDE |
| Oksafenamide |
| enidran |
| N-Salicoylaminophenol |


 CAS#:20978-99-8
CAS#:20978-99-8
