| Description |
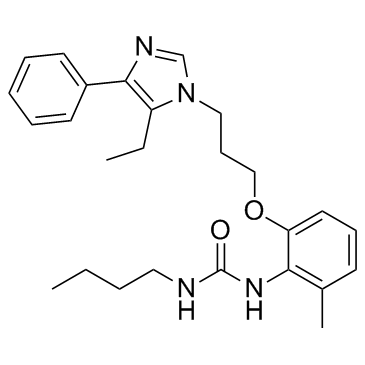
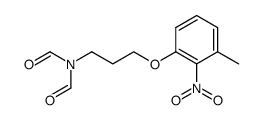
E-5324 is potent inhibitor of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) with IC50s of 44 to 190 nM.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
IC50: 44 to 190 nM (ACAT)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
E-5324 is a potent ACAT inhibitor with IC50s of 44 to 190 nM in microsomes. E-5324 shows no effect on triglyceride synthesis up to 10 μM. E-5324 also has no effect on bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase or lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) up to 10 μM. E-5324 inhibits the incorporation of [3H]oleate into cholesteryl [3H]oleate in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.44 μM. E-5324 also inhibits [3H]cholesteryl ester synthesis with an IC50 of 0.41 μM[1].
|
| In Vivo |
The areas under the cholesterol-time curves for duration of this study (AUC) for control, E-5324 0.02% and E-5324 0.1% are 104985±4411, 106096±4476 and 105231±4 348 mg×day/dL, respectively. The high dose of E-5324 (0.1%) significantly reduces the surface involvement by 34% and 54% in the aortic arch and thoracic aorta, respectively. E-5324 treatment significantly reduces the wet weight and protein content. In the aortic arch, the high dose of E-5324 (0.1%) significantly reduces both cholesteryl ester and total cholesterol by 60% and 59%, respectively. The high dose of E-5324 (0.1%) markedly reduces the ACAT activities in the aortic arch and thoracic aorta by 35% and 44%, respectively[2].
|
| Cell Assay |
In the study of the inhibitory effect of E-5324, PMA-treated THP-1 cells are incubated in LPDS/RPMI containing 50 μg protein/mL βVLDL for 5 hr. Then, 100 μL of each concentration of E-5324 solution or vehicle (LPDS/RPMI) is added to the cultured cells. After incubation with E-5324 for 30 min, 20 μL of [3H]oleate-BSA complex is added, and the mixture is incubated for 2 hr. The lipids are extracted from the cells with hexane: 2-propanol (3:2, v/v) and then separated by TLC. The remaining cellular protein is dissolved in 0.1 N NaOH[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Forty male WHHL rabbits weighing approximately 1.7 kg at the age of 3 months are used in the experiment. All animals are individually caged and receive 100 g/day of food throughout the experiment. The rabbits are divided into 4 groups so as to make their plasma total cholesterol levels similar. The rabbits are fed a standard rabbit chow, ORC-4, or ORC-4 containing E5324 (0.02% or 0.1% (w/w)), or ORC-4 containing probucol (1% (w/w)) for 16 weeks[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Kogushi M, et al. Effect of E5324, a novel inhibitor of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase, on cholesteryl ester synthesis and accumulation in macrophages. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;68(2):191-9. [2]. Kogushi M, et al. Anti-atherosclerotic effect of E5324, an inhibitor of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase, in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1996 Aug 2;124(2):203-10.
|